Tackle Diseases by Sculpting Epigenome
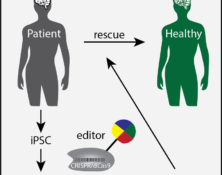
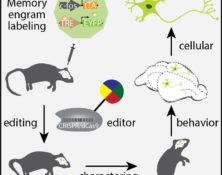
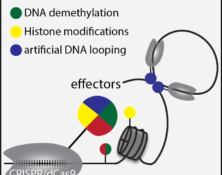
Many human diseases are intermingled by the genetic mutations and environmental influences. Brain, the most complex organ in humans, is vulnerable to genetic mutations as well as extreme environmental stimuli. As the coordinator between the genome and the environment, the epigenome undergoes dynamic changes during brain activities. Several epigenetic modifier genes have been shown to play critical roles in brain functions by orchestrating the transcription network in response to environmental stimuli. Alterations of the epigenome have been observed in many types of brain disorders (Landgrave-Gomez et al., 2015), and the reversibility of epigenetic events has triggered substantial enthusiasm to tackle these brain disorders via epigenome editing approaches. With application of the DNA methylation editing tool we developed, we studied the hypermethylation of the CGG repeat expansion mutation at the 5’ UTR of fragile X mental retardation 1 (FMR1) gene. We demonstrated that demethylation of the CGG repeats unlocked the epigenetic silencing of FMR1 and restored FMRP expression in FXS cells (Liu et al., 2018). Currently, with support from Rett Syndrome Research Trust, we are applying a new epigenome editing strategy to reactivate the wild type allele of MECP2 in the inactive X chromosome (Xi) of Rett Syndrome (RTT) patient-derived cells. Reactivation of the MECP2 allele in the Xi represents a new challenge as multiple layers of epigenetic repressive mechanism are involved. We are developing two additional tools allowing for targeted histone modification and artificial DNA loop. Combination of DNA methylation editing and additional epigenetic manipulations enabled by these new tools resulted in a reactivation of MECP2 in the Xi. Edited RTT neurons showed a functional rescue on soma size and electrophysical defects. We plan to apply this combination editing strategy to study other human diseases associated with epigenetic events.
Ref:
Landgrave-Gomez, J., Mercado-Gomez, O., and Guevara-Guzman, R. (2015). Epigenetic mechanisms in neurological and neurodegenerative diseases. Frontiers in cellular neuroscience 9, 58.
Liu, X., Jiao, B., and Shen, L. (2018). The Epigenetics of Alzheimer’s Disease: Factors and Therapeutic Implications. Front Genet 9, 579.